Liabilities and stockholders’ equity balance sheet wileyplus – Liabilities and stockholders’ equity are fundamental components of a company’s financial health, providing insights into its financial obligations and ownership structure. Understanding their interplay is crucial for investors and analysts alike, enabling them to make informed decisions about a company’s financial stability and growth potential.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of liabilities and stockholders’ equity, examining their individual characteristics and their collective impact on a company’s financial well-being.
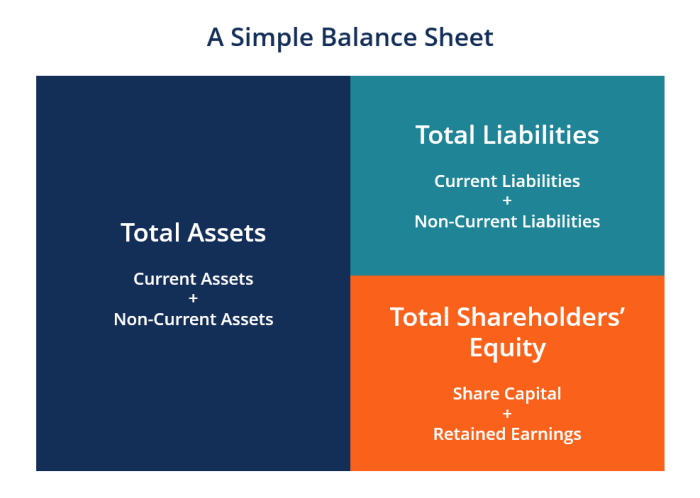
Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity on the Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial health at a specific point in time. It is divided into two main sections: assets and liabilities and stockholders’ equity.
Liabilities are obligations that a company owes to other entities. They can be short-term, such as accounts payable, or long-term, such as bonds payable. Liabilities are presented on the balance sheet in order of their maturity date.
Stockholders’ equity is the residual interest in the assets of a company after all liabilities have been paid. It represents the ownership interest of the company’s shareholders.
Examples of Liabilities
- Accounts payable
- Notes payable
- Bonds payable
- Deferred revenue
- Accrued expenses
Importance of Understanding Liabilities
Understanding liabilities is important for financial analysis because they can provide insights into a company’s financial health. For example, a company with a high level of liabilities relative to its assets may be at risk of default.
Stockholders’ Equity and its Components: Liabilities And Stockholders’ Equity Balance Sheet Wileyplus
Stockholders’ equity is the residual interest in the assets of a company after all liabilities have been paid. It represents the ownership interest of the company’s shareholders.
The key components of stockholders’ equity are:
- Common stock
- Preferred stock
- Retained earnings
Common stock is the most common type of stock. It represents the ownership interest of the company’s common shareholders.
Preferred stock is a type of stock that has a preference over common stock in terms of dividends and liquidation.
Retained earnings are the profits that a company has earned and retained over time.
Changes in Stockholders’ Equity
Stockholders’ equity can change over time due to a number of factors, including:
- Issuance of stock
- Repurchase of stock
- Payment of dividends
- Earnings
- Losses
Relationship between Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity
The relationship between liabilities and stockholders’ equity is inverse. As liabilities increase, stockholders’ equity decreases, and vice versa.
This is because liabilities represent obligations that a company owes to other entities, while stockholders’ equity represents the ownership interest of the company’s shareholders.
A company with a high level of liabilities relative to its stockholders’ equity may be at risk of default.
Implications of High Levels of Liabilities, Liabilities and stockholders’ equity balance sheet wileyplus
High levels of liabilities can have a number of negative consequences for a company, including:
- Increased risk of default
- Higher interest rates on debt
- Reduced access to capital
Use of Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity in Financial Analysis

Liabilities and stockholders’ equity are two important factors that are used in financial analysis.
Financial ratios that incorporate liabilities and stockholders’ equity can provide insights into a company’s financial health. For example, the debt-to-equity ratio measures the amount of debt a company has relative to its stockholders’ equity.
Other financial ratios that use liabilities and stockholders’ equity include:
- Times interest earned ratio
- Return on equity
- Return on assets
These ratios can help investors and analysts evaluate a company’s financial health and make informed investment decisions.
FAQ Explained
What is the difference between liabilities and stockholders’ equity?
Liabilities represent a company’s financial obligations, while stockholders’ equity represents the residual interest in the assets of the company after deducting liabilities.
How do liabilities affect stockholders’ equity?
An increase in liabilities leads to a decrease in stockholders’ equity, as the company’s net assets are reduced.
What are some examples of liabilities?
Examples of liabilities include accounts payable, notes payable, and bonds payable.